Fog Computing vs. Edge Computing
Fog and edge computing lie just upon the periphery of the cloud, but how can they enhance the way data is processed? With a name coined from meteorological origins, fog computing focuses on the space of data area between the source and the cloud. Edge computing, on the other hand, centers where data is collected. The key difference between edge and fog is in the location of intelligence and computing power.
What is Fog Computing?
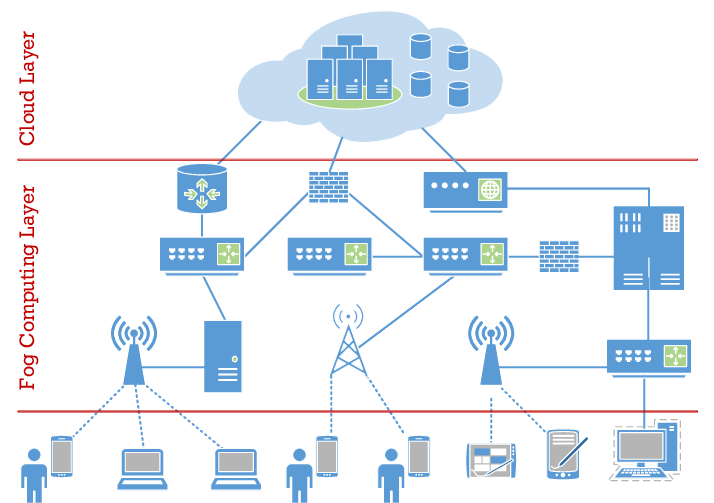
While fog and edge computing are commonly used interchangeably, there are some nuanced significances that separate them from each other. In a foggy environment or the fog layer (Figure 1), intelligence is located at the local area network (LAN). Data is transmitted through Fog gateways where it is then transmitted to sources for processing. In cases where cloud computing cannot support the large volume of data of IoT and IIoT devices, fog is a worthy alternative. Fog’s architecture is comprised from a series of nodes in which IoT devices can receive data in real-time (the goal is to limit latency to one millisecond).
Figure 1: Fog computing architecture
Source: ResearchGate
The Advantages of Fog Computing:
In terms of benefits, Fog’s multitude of data points that feed into Fog provides a more scalable view than Edge computing might. Other benefits of Fog computing include:
- nserves the amount of data that is transmitted to the cloud, resulting in bandwidth reduction.
- improves latency times as initial data processing occurs near its source
- og computing is LAN based, the network has the connectivity flexibility to be wired, work over Wi-Fi, or 5G (must be high speed connectivity)
Disadvantages of Fog Computing:
- computing is tethered to a physical location
- Fog may impose potential security threats in IP spoofing and Man in the Middle Attacks
- Startup costs surrounding fog may inhibit implementation as fog requires the incorporation of both edge and cloud solutions
- While fog was defined by Cisco several years ago, there is still some ambiguity surrounding fog and its vendors
Fog Computing Use Cases:
- Traffic Control Devices
- Autonomous Vehicles
What is Edge Computing?
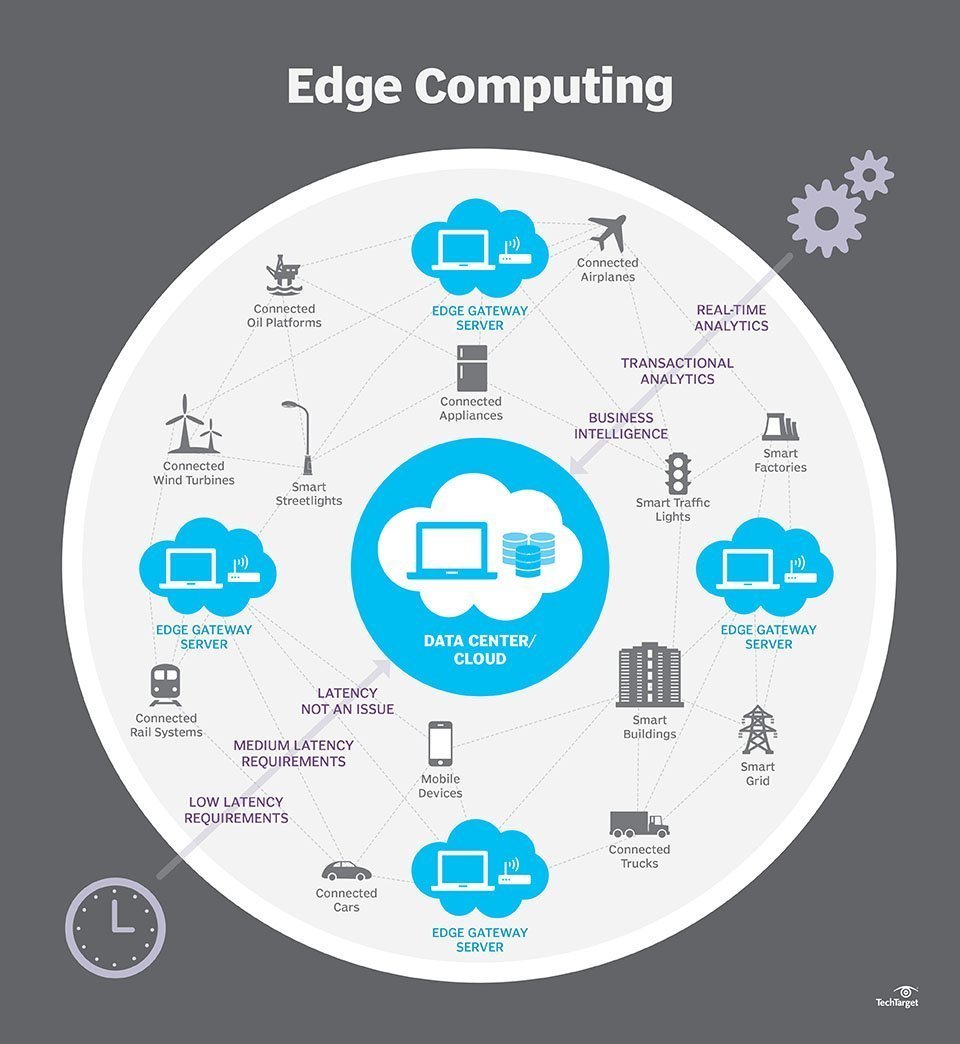
As opposed to fog, edge’s intelligence (Figure 2) is located where data is generated. Edge servers and storage are installed on a device to collect and process data produced by sensors within the device. The processed data can then be transmitted to another data center for human review, archival, merged, and analyzed for broader analytics.
Edge computing is decentralized in nature and demands high levels of monitoring and control. Edge offers an effective solution to emerging network problems associated with transmitting large volumes of data that IoT and IIoT corporations produce. However, edge computing does not have the compute and storage that is necessary to perform advanced analytics. While cloud computing can perform advanced analytics, it is too far away from the source to process and respond in a real-time manner.
Figure 2: Edge architecture
Source: Tech Target
Advantages of Edge Computing:
- Edge is a flexible connectivity solution in remote areas
- Data can be kept close to its source and within the bounds of data sovereignty laws
- Offers advanced security as data traversing the network back to the cloud can be secured through encryption
Disadvantages of Edge Computing:
- Scope and purpose of edge deployment must be clearly defined and specific – limited capability
- Connectivity solutions for edge deployments must accommodate poor or erratic connection
- Entities must decide the fate of unnecessary data after analyses are performed
Edge Computing Use Cases:
- Oil rigs
- Ships at sea
- Remote farms
- Manufacturing
- Network optimization
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Transportation
Interested in incorporating cloud, edge, or fog computing into your data processing logistics? Contact Symmetry Electronics today!